UV ink composition and characteristics
In order to understand the latest technological advancement of UV inks and the improvement of the specific use performance of UV inks, it is helpful to grasp the basic knowledge of ink chemistry. UV ink formulations are mainly monomers and oligomers. The monomer is a low molecular weight reactive diluent that produces a homogeneous solution that imparts surface characteristics to the ink. There are three types of monomers: low-activity monofunctional monomers, moderately active bifunctional monomers, and trifunctional monomers. The trifunctional monomer cures fastest and produces the hardest surface. The monomer is 100% solid and does not release volatile organic compounds like solvents. Once the monomers are cured, they become part of the polymer matrix of the ink film.
Monomers impart the surface properties of the ink, and the oligomers determine the final properties of the cured ink layer, including flexibility, weatherability, and chemical resistance. The oligomers have a high molecular weight and form the main chemical entity of the UV ink. It has several kinds, there are epoxy acrylate, polyester, polyurethane and other kinds. When cured, they are linked differently at the molecular level. Acrylic type is most commonly used in screen printing inks because of its versatility.
Photoinitiators are important components for the initiation and completion of UV curing. They absorb the UV energy that the light source accumulates on the surface of the print. The UV energy causes the photoinitiator to split into active materials. These reactive materials then initiate the chemical reaction, ie, the polymerization reaction. Polymerization converts liquid inks into solid ink layers. There are two commonly used photoinitiators for screen printing inks: free radical photoinitiators and cationic photoinitiators.
UV light does not have enough energy to allow the active molecules in the ink layer to interact to generate free radicals. Therefore, a free radical photoinitiator should be added to the formulation. When photoinitiator molecules are exposed to certain wavelengths of UV light, they absorb light to generate free radicals, initiate cross-linking reactions, and as a result, undergo transient polymerization. Radical photoinitiators are most commonly used for more than 90% of UV screen printing inks.
UV inks formulated with cationic photoinitiators generally contain monomers and oligomers that are different from those formulated with free radical photoinitiators, but the true difference between these inks lies in the way photoinitiators react. Cationic photoinitiators are generally aryl tetravalent sulfide salts that, when exposed to UV light, generate an acid catalyst that initiates the polymerization reaction. Unlike the chemistry of free radicals, the cation reaction will continue after removing the UV light. Cationic photoinitiators account for only 5% to 8% of screen printing UV inks.
The physical state of the ink after curing is greatly affected by the light source structure. The final performance of the cured ink layer depends on the following four main factors:
1, UV radiation, expressed in mW/cm2
2, spectral output, UV light wavelength unit is nm
3, UV energy, expressed in mJ/cm2
4, infrared energy or heat
The latest UV inks have better hiding power and the thick ink layer can also be cured. It is no longer important to understand what UV exposure is and how it acts on the ink. There are many interactions between UV screen printing inks and UV lamps, all of which affect the performance of the finished ink and determine the optimal configuration of the curing device.
The two key factors in the curing process are the amount of radiation and energy that printers often measure but often misunderstand. The amount of radiation is the radiant power reaching the surface of the ink. The peak value of the radiation is the highest power value. It occurs at the focus of the UV light. If the reflector of the curing device does not collect light well, the amount of radiation is lower than the optimum value. It is the decrease of the curing speed or the insufficient curing of the ink layer.
UV energy is the product of two independent variables, radiation dose and time, and 1 watt per second equals 1 Joule of radiant energy. Radiation energy is generally mentioned when there is no indication of the amount of radiation, and the combination of the two will produce the best curing conditions. When curing pigments with high content, opaque inks, or thick ink layers, higher amounts of radiation have a greater effect on curing than energy.
Together with photoinitiator suppliers, ink formulators have developed inks that match the UV output of medium-pressure mercury vapor lamps. These lamps are used in most curing equipment for screen printing. Photoinitiators designed for pigment inks generally absorb wavelengths of 330 to 400 nm. For ink formulators, two different properties of the photoinitiator absorption curve must be taken into account.
1. Which wavelength of light is absorbed?
2. What is the intensity of absorption?
It is important to understand that all components of UV inks absorb UV energy but absorb different wavelengths. This concept is illustrated in Figure 1 and compares the absorption of pigmentless UV inks with pigment inks.
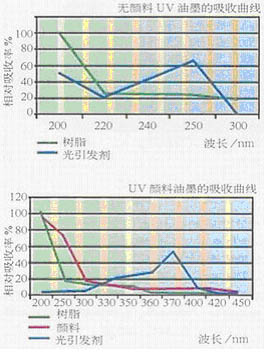
Figure 1 The UV component of the ink composition varies greatly. The above table illustrates this. Pigments and resins are affected by shorter UV wavelengths, photoinitiators are more pronounced for longer absorption
Opaque pigment inks react differently to UV radiation and energy peaks and UV spectra than non-pigmented UV varnish. Photoinitiators developed for the pigment coating cure generally have higher light attenuation coefficients at longer wavelengths (300-450 nm) than clear coatings. Longer-wavelength light is required for thick UV coatings to achieve full cure, so bulbs It is important that the characteristics match the properties of the coating to be cured. This method optimizes cure speed and overall productivity.
Screen printing equipment manufacturers have also improved their technology, resulting in increased production of machines and shorter installation times. Because of the demand for speed, ink manufacturers have to develop inks with low UV exposure and fast curing speed. Formulating inks that match the spectral output of lamps is the key to successful high-speed printing.
With the latest developments in digital printing, it is envisaged that screen printing will be eliminated, but technical breakthroughs in UV-cured screen printing inks are continuously establishing new performance standards and increasing the speed of digital printing and screen printing. The threshold of competition in versatility. At present, UV screen printing inks can be used in a variety of special products, so that the product has a diverse and decorative appearance, these are beyond the digital 4 color printing.
In the early days of the development of UV inks, the selectivity of the chemical raw materials for formulating the ink was very small, limiting the development of the ink and the scope of application of the ink. In the past 10 years, the function of UV inks has been expanded, raw material suppliers have shown greater interest in the ink market, and today's ink manufacturers can choose from thousands of raw materials. With these improvements, the cooperation between raw material suppliers and ink manufacturers has resulted in many new and innovative inks dedicated to screen printing. The latest developments are as follows:
â— Thermoformable UV ink
â— Large range of UV inks for various applications (can be used for printing containers, POP images, flags, and signs)
â— Thick ink UV ink, such as special flash ink, thixotropic special effect ink, liquid molding substrate ink / electrostatic ink
â— Magnetic UV ink
â— Flame retardant UV ink
â— High hiding power UV ink
â— Water resistant UV ink
â— special effects imitation metal UV ink
â—Long-lasting UV ink
Compostable Tablewares,Disposable Cutlery Tablewares,Biodegradable Dishware,Compostable Tableware
Anhui Jianfeng Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.ahbiocutleries.com