First, the status of polycarbonate in the reproduction of optical discs
As an engineering plastic, polycarbonate has low water absorption, high light transmittance, high heat resistance and high strength, and has a wide range of applications. Polycarbonate was originally classified into calendering and injection molding grades. As a polymer plastic, the calendering grade has the highest degree of polymerization and therefore has the highest molecular weight. It is used in the production of sheet metal, pipe, and other calendered products, such as the sun board is one of them. Injection molding grade has a medium degree of polymerization, so the size of the molecular weight is also medium, and it is used for injection molding various mechanical and electrical parts and daily necessities.
In 1982, Polygram Records and Sony Records of Japan took the lead in using low-molecular-weight polycarbonate to produce CDs. Since then, there have been new disc-grade polycarbonate plastics that are specially used for optical disc duplicating and processing. Other transparent plastics such as plexiglass (PMMA), which was once used for LP-reflex TV, and rigid PVC plastics, are not considered for CD-replication. CD-grade polycarbonate's low water absorption, high light transmittance, high heat resistance and high degree of performance, can meet the high-precision and birefringence requirements of optical disc molding, good fluidity not only ensures high-precision replication, And it shortens the production cycle and improves the production efficiency.
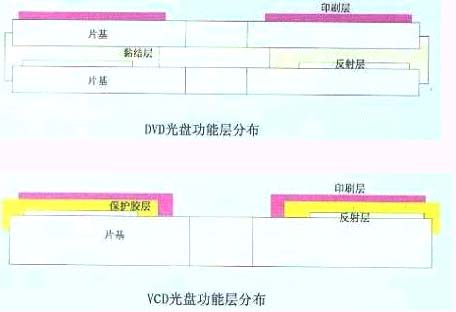
From the perspective of the geometry of the optical disc, at least 93% of the entire disc is a polyphosphate material. According to the standard, the thickness of the disc is 1.2 mm. Take CD as an example, the thickness of the reflective layer aluminum is only 0.00055 mm, the thickness of the protective adhesive is about 0.010 mm, even the thickest 5 layers of screen printing thickness is about 0.05 mm, in addition, the CD disc There is a small circle of protection rubber on the outer edge and the center of the pit, because in order to save the polycarbonate, some CD discs have a thickness of close to 1.1 mm. Even so, at least 93% of the weight of each disc is polycarbonate. ester. Compared with CDs, DVD discs have a protective layer of about 0.010 mm, but the thickness of the adhesive layer and reflective layer is less than 0.010 mm. The thickness of two DVD substrates is strictly around 0.6 mm. Therefore, At least 93% of the weight of each DVD disc is polycarbonate.
Second, the status quo of discarded disc recycling
The global optical disk copy factory processes 25 billion optical discs a year, resulting in more than 1 billion discs discarded, reaching 15,000 tons per 15 grams, plus 25 billion injection ports (according to 0.4 grams per frame) and A small amount of polycarbonate blocks about 10,000 tons, so the disc industry scrapped more than 25,000 tons of polycarbonate each year, accounting for 5% of the global supply of polycarbonate for optical discs. This does not include discs discarded by software vendors and publishers of audio and video products, pirated discs captured by the government, and the number of discs discarded after normal use.
The injection port and a small amount of polycarbonate block in the optical disc replication factory can be recycled in principle after cleaning is very clean, generally used after re-granulation. There are also many CD copy factories that install the injection port smash recovery device on an optical disk injection molding machine. Because they are not contaminated, they are directly mixed with new materials to produce the optical disk base. This method is more expensive and is more expensive than the production CD-R disc production line. More; At present, the price of polycarbonate used for CDs has increased significantly. This is also one of the methods that can be considered.
The copyright of pre-recorded disc orders accepted by the CD-copying factory is owned by the publisher, and a substantial portion of the discarded discs can still be replayed. In order to protect the intellectual property rights of customers, discarded discs are usually crushed and sold (some customers even ask to crush into pieces in the production area before they can be sent to the waste warehouse), or they can trust the factory to destroy them completely. Information, to ensure that the customer's intellectual property will not be lost. The shredded disc fragments have lost the form of the entire disc, and it is difficult to remove the non-polycarbonate material layers—reflective layers, protective adhesive layers and print layers—by mechanical means. Chemical treatment of discarded discs has become almost the only option.
The so-called chemical method is to use a reaction of the reflective layer with an alkali or an acid to dissolve the reaction product of the reflective layer into the solution while peeling off the protective adhesive layer (or the adhesive layer) and the printed layer. For example, reacting caustic soda (NaOH) with aluminum to form sodium metaalumina dissolved in water, stripping the protective layer and printing layer on the CD; reacting nitric acid with silver to produce silver nitrate dissolved in water, making the CD-R The protective adhesive layer and the print layer are peeled off; there is also the use of caustic soda solution at a certain temperature to react with the DVD disk to peel off the print layer and the like. (to be continued)
Ice pack,cold pack,cooling pack,Gel cold pack
Ningbo Hejia Ice pack co. LTD, , https://www.cooling-pack.com