Potential risks of coatings in metal food packaging containers under high temperature conditions
Lai Hongjuan, Lai Hongxia, Xie Yongping, Liao Huimei, Chen Weiping
In recent years, the domestic consumer market is starting. According to the survey conducted by China Food Industry Association, with the improvement of residents' living standards, the concept and mode of food consumption are quietly changing. Travel and travel are increasing. Canned food is adapting to people's convenience, hygiene and storage. Everyday needs are welcomed by people.
The packaging of canned food is generally a metal packaging material, and the metal packaging container is a small-capacity container made of a thin metal plate, and can be classified into a metal container such as aluminum, steel or tinplate according to the material. In order to prevent rust and corrosion, metal cans used for food packaging generally spray food coatings on the inner wall, such as epoxy phenolic coatings and water-based modified epoxy coatings, to isolate electrochemical corrosion and heavy metals in metal cans and contents. Migration plays a role in protecting food safety and increasing shelf life. Harmful substances in the coating of food can affect the amount of hormones in the human body, leading to disorders of the endocrine system, affecting reproductive, developmental and other functions, and even causing malignant tumors, leading to biological extinction. At present, there are related research reports on harmful substances in the inner coating of food cans, but the impact of the sterilization process on the harmful substances of the coating has not been found. Since metal cans generally require a sterilization process when storing food. The coating of the metal can and its inner wall also goes through the sterilization process. Whether the safety of the inner wall coating meets the requirements of high temperature and high pressure in the sterilization process cannot be ignored. In this regard, this paper studies the food packaging containers coated with epoxy phenolic coatings and water-based modified epoxy coatings, comparing the migration conditions (95 ° C, 30 min) and high temperature conditions (121 ° C, 30 min) required by the sanitary standards. The migration results analyzed the potential risks of coatings in metal food packaging containers under high temperature conditions.
1 Experimental part
1.1 Main reagents and instruments
Acetic acid, olive oil: analytical grade, Guangzhou Chemical Reagent Factory; distilled water: Guangzhou Zhongsheng Haohao Beverage Co., Ltd.
Dual-beam UV-Vis spectrophotometer: UV2450, Shimadzu Corporation, Japan; Liquid Chromatograph: 1200 Series, Agilent, USA; Electronic Analytical Balance: BSA224S-CW, Sartorius, Germany, Sensing 0.1mg; Autoclave: HVE- 50, Japan Hirayama.
1.2 Test indicators
The risk indicators of this test include free phenol, free formaldehyde, potassium permanganate consumption and bisphenol A. The conditions were tested at 95 °C/30min and 121 °C/30min respectively. The specific indicators and corresponding detection methods are shown in the table. 1.
Table 1 Monitoring risk indicators and testing methods
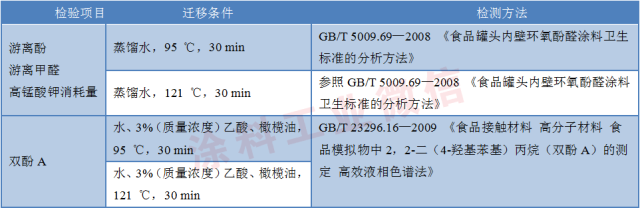
1.3 Sample composition
The total sampling batch for this test was 20 batches from 12 manufacturing companies. Water-based modified epoxy resin coating and epoxy phenolic coating each 10 batches. The samples tested were from the manufacturer's stock or finished product library.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Analysis of detection results of free phenol
The test results of free phenol are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Test results of free phenol
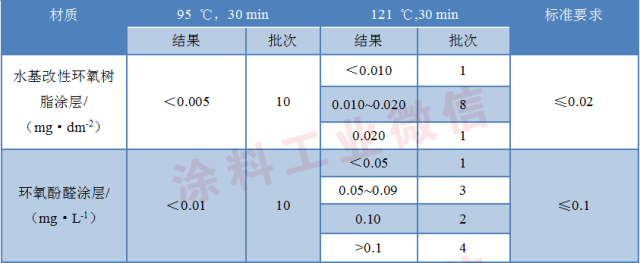
The hygienic standard for water-based modified epoxy resin coating is GB11677-2012 "Food Safety National Standard Water-Based Modified Epoxy Resin Coating for Cans". The requirement for free phenol is not more than 0.02mg/dm2. 2 It can be seen that in the 10 batches of samples tested in this test, the results are all less than 0.02mg/dm2 according to the standard immersion conditions (95°C, 30min); and the results are tested when tested at 121°C for 30min. Out, the result of one batch is 0.020mg/dm2. If it is compared with the requirements of GB11677-2012, it has already appeared in the critical value required by the standard, it is worth noting.
The hygienic standard for epoxy phenolic coating is GB4805-11994 "Sanitary standard for epoxy phenolic coating on the inner wall of food cans". The requirement for free phenol is not more than 0.1 mg/L. From Table 2, 10 batches of this test are known. The secondary samples were tested according to the standard immersion conditions (95 ° C, 30 min), the results were less than 0.1 mg / L; and the test was carried out at 121 ° C, 30 min, the results were detected, and there are 4 batches of results More than 0.1mg / L; the results of the two batches is 0.1mg / L, if compared with the standard requirements of GB4805 - 1994, 40% of the results are greater than 0.1mg / L.
2.2 Analysis of detection results of free formaldehyde
The test results of free formaldehyde are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Test results of free formaldehyde
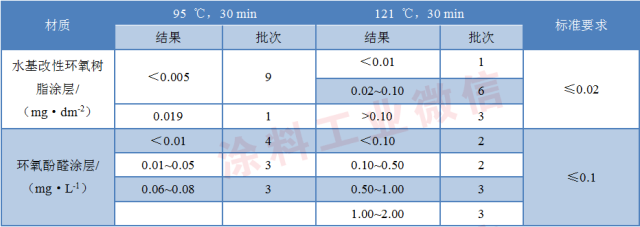
It can be seen from Table 3 that in the test of free formaldehyde, the detection result at 121 °C is much higher than that at 95 °C. The results measured at 95 ° C for 30 min are in compliance with the standard requirements, and are measured at 121 ° C for 30 min. As a result, 90% of the water-based modified epoxy resin coating is greater than 0.02 mg/dm2. If judged according to the standard, the failure rate is 90%, and the highest test result is 0.125 mg/dm2, which is higher than the standard requirement. It is 6 times higher; 80% of the epoxy phenolic coating results are greater than 0.1 mg/L, and the highest test result is 1.92 mg/L, which is 19 times higher than the standard requirement. Mainly because formaldehyde is easily released during hot pressing, which poses a threat to human health.
2.3 Analysis of detection results of potassium permanganate consumption
The test results of potassium permanganate consumption are shown in Table 4.
Table 4 Test results of potassium permanganate consumption
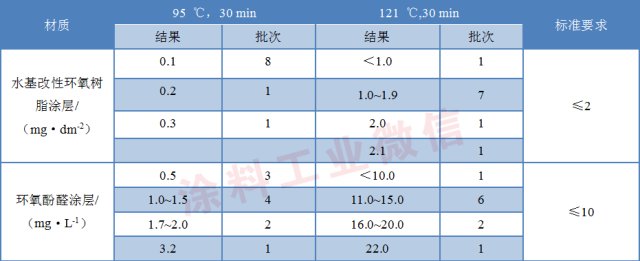
The test results of potassium permanganate consumption mainly indicate the content of soluble organic substances. It can be seen from Table 4 that in this test, the detection result of potassium permanganate consumption of 121 ° C is much higher than that of 95 ° C. The results of measurement at 95 ° C for 30 min are in line with the standard requirements, and according to 121 At °C, 30min, the water-based modified epoxy resin coating has 20% greater than 2mg/dm2. If judged according to the standard, the failure rate is 20%; the epoxy phenolic coating has 90% result. Above 10mg/L, the highest test result is 22.0mg/L, which is 2 times higher than the standard requirement.
2.4 Analysis of monitoring results of bisphenol A
The soaking conditions designed in this test, whether it is 95 ° C, 30 min, or 121 ° C, 30 min; whether water, 3% acetic acid, or olive oil, the bisphenol A of the 20 batch samples tested were not detected, it can be seen The bisphenol A migration of these products is satisfactory.
2.5 Risk Analysis
2.5.1 Exposure calculation model
In this risk study, the risk analysis method calculates the daily cumulative exposure by referring to the US safety evaluation method, that is, by performing a migration test to calculate the daily cumulative exposure (EDI), and the calculation formula is as shown in the formula (1).
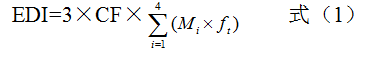
Where: EDI is the estimated daily intake [mg / (kg · d)]; 3 is assumed to consume 3 kg of packaged food per person per day, and packaging material corresponding to 1 kg of food 6dm2; CF - packaging material consumption factor; Ft—the proportion of food type (water, acid, alcohol, ester) in all foods; Mi—the concentration of the migratory substance in the food simulant. According to the data, the consumption factor CF of the metal coating is 0.17, the food distribution factor ft water is 0.16, the acid is 0.35, the alcohol is 0.40, and the ester is 0.09.
2.5.2 Exposure of free formaldehyde in metal coatings
Since formaldehyde has the best solubility in water, this study calculates EDI according to the most severe conditions, that is, the amount of formaldehyde migration in water instead of the formaldehyde migration of other types of food. According to the above model, combined with the migration of free formaldehyde obtained by this risk monitoring, the highest detection result of water-based modified epoxy resin coating is 0.125mg/dm2 at 121 °C for 30 min, and the epoxy phenolic coating is the highest. The test result was calculated at 1.92 mg/L. The exposure amount of formaldehyde in the water-based modified epoxy resin coating was 0.38 mg/kg, and the exposure amount of formaldehyde in the epoxy phenolic coating was 0.98 mg/kg. The greater the cumulative daily exposure, the greater the risk, the four levels of cumulative exposure on the control day: the first level <0.5μg/kg; the second level 0.5~50μg/kg; the third level 50μg/kg~1mg/kg The fourth level is >1mg/kg; it can be exempted from management when it is at the first level, and it is recommended to be approved by food additives when it is at the fourth level. The exposure of formaldehyde in the metal coating is at the third level and close to the fourth level. Limits, which are potentially risky, should be taken seriously.
2.5.3 Exposure of potassium permanganate consumption in metal coatings
The consumption of potassium permanganate is the total amount of organic matter dissolved in the food package. At present, the detection method in China can only carry out migration experiments with water. There is no related detection method for other mimics. Therefore, this study only calculates the consumption of potassium permanganate in aqueous food. The cumulative daily exposure of the amount was 0.14 mg/kg for the water-based modified epoxy resin coating at 121 ° C for 30 min, and the EDI of the epoxy phenolic coating was 0.60 mg/kg. Both are at the third level and are potentially risky and equally worthy of attention.
2.5.4 Exposure of free phenol and bisphenol A in metal coatings
Since the migration amount of free phenol and bisphenol A is relatively low, the exposure amount is small and the risk is not large.
3 Conclusion
Among the monitored items, the consumption of free phenol, free formaldehyde and potassium permanganate was 3 items. The test results under high temperature conditions (121 ° C, 30 min) were higher than the migration conditions specified in the standard requirements (95 ° C, 30 min). result. And the test results under most high temperature conditions are higher than the standard requirements, especially the daily cumulative exposure of formaldehyde migration and potassium permanganate consumption is relatively high, it can be seen that the metal inner coating exists under high temperature conditions (121 ° C, 30 min). Potential risks. Although the inner coating of metal food packaging containers is inspected according to sanitary standards before use, the inner coating of metal food packaging containers needs to undergo high temperature sterilization process in the actual use process, and harmful substances migrated under high temperature conditions, For example, free formaldehyde and other organic substances will migrate into foods, thus affecting people's health. Therefore, the hazards brought about by the high temperature sterilization process cannot be ignored.
(1) It is recommended that the production enterprises use high-quality raw materials as much as possible, and the residual amount of harmful substances after processing high-quality raw materials is relatively small, and at the same time increase the control of production equipment, production processes and working conditions of production workers, and regulate Production, improve product quality.
(2) It is recommended that the manufacturer who needs the high temperature sterilization process test the outer packaging (metal can inner coating) used before use according to the conditions of the process to ensure the safety of the outer packaging during use.
(3) In terms of sterilization technology, the manufacturer should understand the spoilage bacteria existing according to the characteristics of the substances contained in the metal cans, and according to the heat resistance characteristics of the bacteria group, calculate the combination of the temperature and time conditions for killing microorganisms in the heat sterilization process, and Specific sterilization process parameters are determined experimentally.
(4) Based on the shortcomings of high temperature sterilization technology, a new sterilization technology, fence sterilization technology, can be used to keep the temperature of the food from changing during the sterilization process, using different fence factors, scientifically and reasonably Combined, they play a synergistic role to suppress microbes that cause food spoilage from different sides, forming a multi-target attack on microorganisms, so that microorganisms in food can not overcome these obstacles, thereby improving food quality and ensuring food hygiene and safety. It not only guarantees that the nutrients in the food materials, as well as its color, taste and fragrance, will not be greatly lost, and also avoids the migration of harmful substances coated in the food can coating to the food during the high temperature sterilization process.
Facial Sheet Mask
Facial Sheet Mask
DELIN HAIR COSMETICS , https://www.skinbeautymaskfactory.com