Shrink wrapping is a method of wrapping products and packages with a heat-shrinkable plastic film and then heating to shrink the film and wrap the product or package; the stretch wrap is made of a stretchable plastic film at room temperature. Wrap the product or package under tension. The principle of these two packaging methods is different, but the resulting packaging is basically the same, they have similar place with the wrapping technology, but the materials and working principles are completely different.
Heat Shrink Packaging Technology Heat shrink packaging technology and thermoforming and body packaging technologies entered the country in the 1970s and have been rapidly developed and popularized. Therefore, it is considered to be one of the three fastest growing packaging technologies in this century. It is also a very promising packaging technology.
First, the commonly used shrink film shrink film is the most important one in the shrink packaging material. According to the characteristics that the thermoplastic plastic recovers under the heating conditions, in the process of forming the film from the plastic raw material, it is stretched by heating in advance and cooled to make a shrink film.
Shrink film manufacturing methods are divided into two types of sheet and tube. The sheet-like film is first made into a sheet, and then stretched along the longitudinal axis and horizontal axis of the film, respectively, said two-stretch method, or simultaneous two-way stretching, said a pull pull method; cylindrical The film is first made into a cylindrical shape and then subjected to secondary stretching or one-time stretching.
1. The main performance indicators of shrink film (1) shrinkage and shrinkage ratio shrinkage including longitudinal and transverse, the test method is the first film length L1, then the film is immersed in 120oС glycerin 1 ~ 2s, remove and cool with cold water , Then measure the length L2 and calculate it as follows:
L1 - L2
Shrinkage (%) = ----- × 100%
L1
In the formula, L1-- is the length of the film before shrinking; L2 is the length of the film after shrinking.
At present, the shrinkage film used for packaging generally requires that the shrinkage ratio in both longitudinal and transverse directions is equal to about 50%; however, in a special case, there is also a one-way shrinkage, and the shrinkage rate is about 25% to 50%. There are also partial extension films that do not have equal longitudinal and transverse shrinkage.
The ratio of shrinkage in both directions is called the shrinkage ratio.
(2) Shrinkage Tension Shrinkage tension refers to the tension applied to the package after the film shrinks. The size of the shrink tension produced at the shrinkage temperature is closely related to the protection of the product. Rigid products such as packaging cans allow for greater shrinkage tension, while some products that are crumbly or easily creased have excessive shrinkage tension and can be deformed or even damaged. Therefore, the shrink tension of the shrink film must be selected properly.
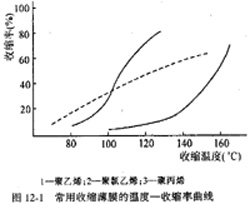
(3) Shrinkage Temperature Shrinkage The film starts to shrink at a certain temperature after it is heated, and the temperature rises to a certain height to stop the shrinkage. The temperature in this range is called the shrinkage temperature. For packaging operations, the package is heated in a heat-shrink tunnel, and the temperature reached when the film shrinks to produce a predetermined tension is referred to as the shrinkage temperature under that tension. Shrinkage temperature and shrinkage have a certain relationship, different films. Figure 12-1 shows the temperature-shrinkage curves of three commonly used shrink films: polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene, and polypropylene. In shrink packaging, the lower the shrinkage temperature, the less adverse effects on the packaged products, especially fresh vegetables, fruits and textiles.
2. Commonly Used Properties and Applications of Shrink Films Currently used shrink films are polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene and polypropylene, polyvinylidene chloride, polyester, polystyrene, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers and chlorinated rubber, etc. .
(1) The shrinkage temperature of PVC shrink film is relatively low and wide, as shown in Figure 12-1. The shrinkage temperature is 40-160°C and the heating channel temperature is 100-160°C. Fast heat shrinkage and good workability. The package is transparent and beautiful after processing, and the heat sealing part is also very clean. Oxygen transmission rate is lower than that of polyethylene, and the moisture permeability is large, so it is more suitable for vegetables and fruits with more moisture content. The disadvantage is that it has a low impact strength, is brittle at low temperatures, and is not suitable for transport packaging. In addition, the sealing seam strength is poor, and the odor is decomposed when heat-sealed. When the plasticizer therein changes, the film is easily broken and loses gloss. At present, PVC film is mainly used for packaging groceries, food, toys, fruits and textiles.
(2) Polyethylene is characterized by its high impact strength, low price, and tight seals. It is used for transport packaging. Polyethylene is less glossy and transparent than polyvinyl chloride. In the operation, the shrinkage temperature is about 20-30° C. higher than that of polyvinyl chloride. Therefore, it is necessary to install a blower cooling device in the rear section of the heat shrinkage channel.
(3) The main advantage of polypropylene is good transparency and gloss, the same as cellophane, good oil resistance and moisture resistance, and strong shrinkage tension. The disadvantages are poor heat sealability, low sealing seam strength, high shrinkage temperature and narrow range. Typical applications are multipacks such as audio tapes and records.
(4) Other thin-film polystyrenes are mainly used for letter packaging, and polyvinylidene chloride is mainly used for meat packaging.
Recently appeared ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer shrink film, high impact strength, high transparency, low softening point, high melting temperature, good heat sealing performance, shrinking tension is small, the packaged product is not easy to damage, suitable for protruding parts The packaging of items or exotic items is expected to have greater development in the future.
Second, the method of shrink packaging Shrink packaging manual heat shrink and mechanical heat shrink packaging two methods, manual heat shrink is usually used to manually wrap the packaged items, and then use hot air gun and other tools on the package blowing hot air, complete Shrink packaging. This method is simple and rapid mainly for packages that are unsuitable for mechanical packaging, such as large-scale pallet-packed products or bulky single-piece shaped products, heat-shrinkable packagings with a thermal power of 1.5×108j/h. A volume of 2m2 product, heat shrink only about 2min. Only one liquefied gas tank can be used in addition to the spray gun. This method is convenient and economical and worth promoting in the country.
Mechanical shrink packaging operations are generally performed in two steps. First, the products and packages are pre-wrapped in a mechanical manner. That is, the products are packed with a shrink film, the necessary mouth and seam are heat sealed, and then the heat shrink is performed. The prewrapped product is placed in a heat shrink device for heating. This method is the most commonly used by us and is therefore the focus of our content.
In the heat shrinkable packaging, the packaging film used for wrapping the article by the heat shrinkable film includes a tubular film, a flat film, and a folded film. The folded film may be formed by cutting a tubular film or may be folded by a flat film. . With tubular film wrap articles, there are few seal seams, but the mechanical wrapper has low efficiency and complicated structure.
1. When prewrapping is pre-packaged, the film size should be 10% to 20% larger than the size of the product. If the size is too small, filling of articles is inconvenient, and the shrinkage tension is too large, and the film may be punctured; if the size is too large, the contraction tension is insufficient, and the bag is not tight or uneven. The thickness of the shrink film used can be determined based on the size of the product, the weight, and the required shrinkage tension.
The commonly used heat shrinkable packaging methods are the following:
(1) Open at both ends: When a tubular film is used, the opening of the film needs to be expanded, and then the product is fed into the tubular film by means of a chute. The size of the film is about 10% larger than the size of the article, as shown in the figure. 12-2 shows. This method is more suitable for wrapping cylindrical objects, such as batteries, paper rolls, wine bottles and so on. The advantage of packaging with a tubular film is to reduce the 1 to 2 sealed seams, and the appearance is beautiful. The disadvantage is that it cannot adapt to the diversification of products, and is usually used for the packaging of single-species and large-volume products.
Heat Shrink Packaging Technology Heat shrink packaging technology and thermoforming and body packaging technologies entered the country in the 1970s and have been rapidly developed and popularized. Therefore, it is considered to be one of the three fastest growing packaging technologies in this century. It is also a very promising packaging technology.
First, the commonly used shrink film shrink film is the most important one in the shrink packaging material. According to the characteristics that the thermoplastic plastic recovers under the heating conditions, in the process of forming the film from the plastic raw material, it is stretched by heating in advance and cooled to make a shrink film.
Shrink film manufacturing methods are divided into two types of sheet and tube. The sheet-like film is first made into a sheet, and then stretched along the longitudinal axis and horizontal axis of the film, respectively, said two-stretch method, or simultaneous two-way stretching, said a pull pull method; cylindrical The film is first made into a cylindrical shape and then subjected to secondary stretching or one-time stretching.
1. The main performance indicators of shrink film (1) shrinkage and shrinkage ratio shrinkage including longitudinal and transverse, the test method is the first film length L1, then the film is immersed in 120oС glycerin 1 ~ 2s, remove and cool with cold water , Then measure the length L2 and calculate it as follows:
L1 - L2
Shrinkage (%) = ----- × 100%
L1
In the formula, L1-- is the length of the film before shrinking; L2 is the length of the film after shrinking.
At present, the shrinkage film used for packaging generally requires that the shrinkage ratio in both longitudinal and transverse directions is equal to about 50%; however, in a special case, there is also a one-way shrinkage, and the shrinkage rate is about 25% to 50%. There are also partial extension films that do not have equal longitudinal and transverse shrinkage.
The ratio of shrinkage in both directions is called the shrinkage ratio.
(2) Shrinkage Tension Shrinkage tension refers to the tension applied to the package after the film shrinks. The size of the shrink tension produced at the shrinkage temperature is closely related to the protection of the product. Rigid products such as packaging cans allow for greater shrinkage tension, while some products that are crumbly or easily creased have excessive shrinkage tension and can be deformed or even damaged. Therefore, the shrink tension of the shrink film must be selected properly.
(3) Shrinkage Temperature Shrinkage The film starts to shrink at a certain temperature after it is heated, and the temperature rises to a certain height to stop the shrinkage. The temperature in this range is called the shrinkage temperature. For packaging operations, the package is heated in a heat-shrink tunnel, and the temperature reached when the film shrinks to produce a predetermined tension is referred to as the shrinkage temperature under that tension. Shrinkage temperature and shrinkage have a certain relationship, different films. Figure 12-1 shows the temperature-shrinkage curves of three commonly used shrink films: polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene, and polypropylene. In shrink packaging, the lower the shrinkage temperature, the less adverse effects on the packaged products, especially fresh vegetables, fruits and textiles.
2. Commonly Used Properties and Applications of Shrink Films Currently used shrink films are polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene and polypropylene, polyvinylidene chloride, polyester, polystyrene, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers and chlorinated rubber, etc. .
(1) The shrinkage temperature of PVC shrink film is relatively low and wide, as shown in Figure 12-1. The shrinkage temperature is 40-160°C and the heating channel temperature is 100-160°C. Fast heat shrinkage and good workability. The package is transparent and beautiful after processing, and the heat sealing part is also very clean. Oxygen transmission rate is lower than that of polyethylene, and the moisture permeability is large, so it is more suitable for vegetables and fruits with more moisture content. The disadvantage is that it has a low impact strength, is brittle at low temperatures, and is not suitable for transport packaging. In addition, the sealing seam strength is poor, and the odor is decomposed when heat-sealed. When the plasticizer therein changes, the film is easily broken and loses gloss. At present, PVC film is mainly used for packaging groceries, food, toys, fruits and textiles.
(2) Polyethylene is characterized by its high impact strength, low price, and tight seals. It is used for transport packaging. Polyethylene is less glossy and transparent than polyvinyl chloride. In the operation, the shrinkage temperature is about 20-30° C. higher than that of polyvinyl chloride. Therefore, it is necessary to install a blower cooling device in the rear section of the heat shrinkage channel.
(3) The main advantage of polypropylene is good transparency and gloss, the same as cellophane, good oil resistance and moisture resistance, and strong shrinkage tension. The disadvantages are poor heat sealability, low sealing seam strength, high shrinkage temperature and narrow range. Typical applications are multipacks such as audio tapes and records.
(4) Other thin-film polystyrenes are mainly used for letter packaging, and polyvinylidene chloride is mainly used for meat packaging.
Recently appeared ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer shrink film, high impact strength, high transparency, low softening point, high melting temperature, good heat sealing performance, shrinking tension is small, the packaged product is not easy to damage, suitable for protruding parts The packaging of items or exotic items is expected to have greater development in the future.
Second, the method of shrink packaging Shrink packaging manual heat shrink and mechanical heat shrink packaging two methods, manual heat shrink is usually used to manually wrap the packaged items, and then use hot air gun and other tools on the package blowing hot air, complete Shrink packaging. This method is simple and rapid mainly for packages that are unsuitable for mechanical packaging, such as large-scale pallet-packed products or bulky single-piece shaped products, heat-shrinkable packagings with a thermal power of 1.5×108j/h. A volume of 2m2 product, heat shrink only about 2min. Only one liquefied gas tank can be used in addition to the spray gun. This method is convenient and economical and worth promoting in the country.
Mechanical shrink packaging operations are generally performed in two steps. First, the products and packages are pre-wrapped in a mechanical manner. That is, the products are packed with a shrink film, the necessary mouth and seam are heat sealed, and then the heat shrink is performed. The prewrapped product is placed in a heat shrink device for heating. This method is the most commonly used by us and is therefore the focus of our content.
In the heat shrinkable packaging, the packaging film used for wrapping the article by the heat shrinkable film includes a tubular film, a flat film, and a folded film. The folded film may be formed by cutting a tubular film or may be folded by a flat film. . With tubular film wrap articles, there are few seal seams, but the mechanical wrapper has low efficiency and complicated structure.
1. When prewrapping is pre-packaged, the film size should be 10% to 20% larger than the size of the product. If the size is too small, filling of articles is inconvenient, and the shrinkage tension is too large, and the film may be punctured; if the size is too large, the contraction tension is insufficient, and the bag is not tight or uneven. The thickness of the shrink film used can be determined based on the size of the product, the weight, and the required shrinkage tension.
The commonly used heat shrinkable packaging methods are the following:
(1) Open at both ends: When a tubular film is used, the opening of the film needs to be expanded, and then the product is fed into the tubular film by means of a chute. The size of the film is about 10% larger than the size of the article, as shown in the figure. 12-2 shows. This method is more suitable for wrapping cylindrical objects, such as batteries, paper rolls, wine bottles and so on. The advantage of packaging with a tubular film is to reduce the 1 to 2 sealed seams, and the appearance is beautiful. The disadvantage is that it cannot adapt to the diversification of products, and is usually used for the packaging of single-species and large-volume products.

